Anatomy and Physiology Lab Practical 1 introduces foundational concepts‚ focusing on microscopy‚ histology‚ and system identification. It provides hands-on experience with human structures and physiological processes.
1.1 Overview of Lab Practical 1
Lab Practical 1 in anatomy and physiology introduces students to foundational laboratory exercises. It covers microscopy‚ histology‚ and the identification of skeletal and muscular structures. Students learn to prepare slides‚ use lab equipment‚ and recognize cellular and tissue structures. Practical exercises include bone and muscle identification‚ with a focus on understanding their functions. This lab serves as a stepping stone for advanced studies‚ ensuring a solid grasp of anatomical and physiological principles through hands-on experience.
1.2 Importance of Lab Practical 1 in Anatomy and Physiology
Lab Practical 1 is essential for developing foundational skills in anatomy and physiology. It bridges theoretical knowledge with hands-on experience‚ enhancing understanding of human structures and functions. Students gain proficiency in microscopy‚ histology‚ and system identification‚ which are critical for healthcare professions. The lab fosters critical thinking‚ observation‚ and manual dexterity‚ preparing students for advanced studies and real-world applications. By mastering these skills‚ students build a strong foundation for understanding complex anatomical and physiological concepts.
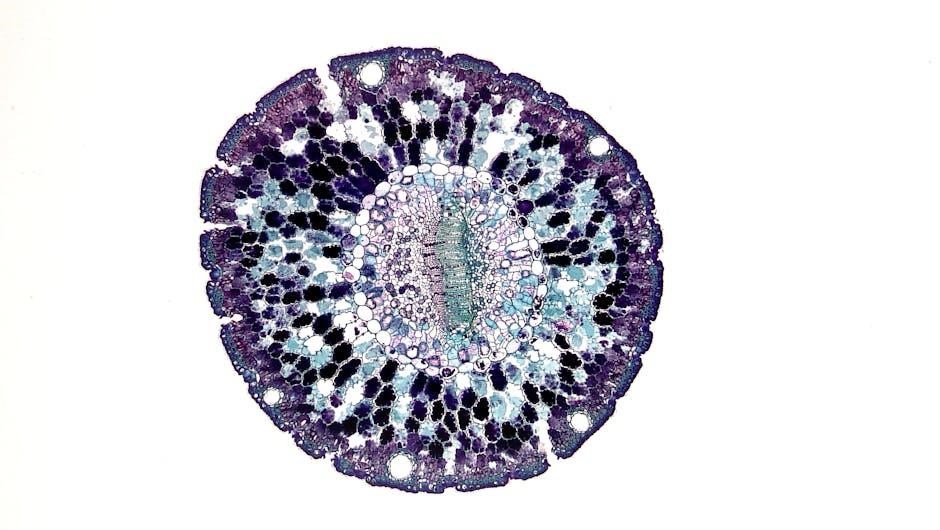
Preparation for the Lab Practical Exam
Preparation involves reviewing study materials‚ practicing microscopy‚ and familiarizing oneself with lab equipment. Focus on key topics like histology and system identification to build confidence and competence.
2.1 Essential Study Materials and Resources
Key study materials include anatomy and physiology textbooks‚ lab manuals‚ and online resources. Textbooks like Guyton and Hall and Chaurasiya’s Anatomy provide detailed insights. Online platforms offering virtual labs‚ histology slides‚ and practice exams are invaluable. Utilize diagrams‚ flashcards‚ and digital tools to reinforce learning. Past papers and practice exams help familiarize yourself with exam formats. Regularly review lecture notes and lab reports to ensure comprehensive preparation. Supplement your studies with educational videos and interactive simulations to enhance understanding of complex concepts.
2.2 Key Topics to Focus On
Focus on mastering microscope parts‚ histology slide preparation‚ and cellular structure identification. Bone classification‚ muscle types‚ and nervous system structures are critical. Understand reflexes‚ nerve impulses‚ and special senses like eye and ear anatomy. Prioritize respiratory and circulatory system components‚ including blood smear analysis; Digestive and urinary system organ identification‚ urinalysis‚ and endocrine gland functions are essential. Familiarize yourself with integumentary system layers and hormone regulation. Practice using dichotomous keys and lab instruments while adhering to safety protocols to ensure exam readiness.
2.3 Lab Setup and Equipment Familiarization
Familiarizing yourself with lab setup and equipment is crucial for efficiency during exams. Understand the microscope‚ including proper handling and maintenance. Learn to prepare histology slides accurately. Practice using dissection tools‚ forceps‚ and scalpels. Know the functions of measuring instruments like calipers and rulers. Familiarize yourself with safety protocols‚ such as handling specimens and chemical solutions. Organize your workspace to ensure quick access to essential tools. Understanding equipment operation enhances your ability to perform tasks confidently and efficiently during the lab practical.
Microscopy and Histology in Lab Practical 1
Mastering microscopy and histology skills is essential for identifying cellular structures and understanding tissue organization. Practice operating microscopes and preparing slides to analyze specimens effectively in the lab.
3.1 Understanding Microscope Parts and Functions
Familiarizing yourself with microscope components is crucial for effective use. Key parts include the eyepiece‚ objective lenses‚ stage‚ light source‚ and focus knobs. The eyepiece and objectives work together to magnify specimens‚ while the stage holds slides securely. The light source illuminates the specimen‚ and focus knobs (coarse and fine) adjust image clarity. Properly understanding and using these parts ensures accurate observations and efficient slide preparation‚ which are essential skills for histology and cellular structure identification in Lab Practical 1.
3.2 Preparing and Examining Histology Slides
Preparing histology slides involves obtaining tissue samples‚ sectioning them thinly using a microtome‚ and staining to enhance visibility. Proper fixation and dehydration ensure tissue preservation. Once slides are mounted‚ they are examined under a microscope to observe cellular structures and tissue organization. Accurate slide preparation and labeling are critical for identifying histological features. This step-by-step process is essential for understanding tissue morphology‚ a key component of Lab Practical 1. Always handle tissues and chemicals with care‚ following safety protocols to avoid contamination or damage.
3.3 Identifying Cellular Structures Under the Microscope
Identifying cellular structures under the microscope requires adjusting the focus and illumination to optimize visibility. Start with low magnification to locate the area of interest‚ then switch to high magnification for detailed observation. Key structures to identify include the cell membrane‚ cytoplasm‚ nucleus‚ and organelles like mitochondria and ribosomes. Proper staining techniques enhance contrast‚ making it easier to distinguish cellular components. Practice recognizing differences between animal and plant cells‚ such as the presence of a cell wall in plant cells. Accurate identification is vital for understanding tissue and organ functions in Lab Practical 1.
Skeletal and Muscular System Identification
This section covers the identification of bones‚ muscles‚ and their roles in movement and structural support‚ with practical exercises for hands-on learning and system integration.
4.1 Bone Identification and Classification
Bone identification and classification involve recognizing different types of bones based on shape and function. Bones are categorized as long‚ short‚ flat‚ irregular‚ or sesamoid. Students learn to identify anatomical features such as the diaphysis (shaft)‚ epiphysis (ends)‚ and articular surfaces. Practical exercises involve distinguishing bones like the femur‚ humerus‚ and vertebrae. Proper classification requires understanding bone structure‚ including compact and spongy bone tissue. This skill is essential for grasping skeletal system anatomy and preparing for lab exams. Using diagrams and 3D models enhances learning and retention of bone morphology.
4.2 Muscle Types and Their Functions
Muscles are classified into three types: skeletal‚ smooth‚ and cardiac. Skeletal muscles are attached to bones‚ enabling voluntary movement and posture. Smooth muscles‚ found in internal organs‚ perform involuntary actions like digestion. Cardiac muscles are specialized for the heart‚ ensuring rhythmic contractions. Each type varies in structure‚ with skeletal muscles being striated and under conscious control‚ while smooth muscles are non-striated and controlled by the autonomic nervous system. Understanding their functions and locations is crucial for identifying them during lab practicals and grasping their roles in the body.
4.3 Practical Exercises for Skeletal and Muscular System
Practical exercises for the skeletal and muscular system focus on identifying bones‚ muscles‚ and their attachments. Students often label skeletal models‚ dissect muscles to observe their structure‚ and palpate major muscle groups on themselves or models. Activities include matching exercises‚ where bones or muscles are identified from diagrams or specimens‚ and analyzing movements to understand muscle functions. These exercises enhance understanding of anatomical relationships and prepare students for lab exams by improving observation and identification skills.
Nervous System and Special Senses
This section explores the nervous system’s structures‚ reflexes‚ and sensory organs. Practical exercises include nerve impulse demonstrations‚ eye and ear dissections‚ and histological examinations of sensory tissues.
5.1 Identifying Nervous System Structures
Identifying nervous system structures involves recognizing key components like neurons‚ glial cells‚ and nerve fibers. Students learn to distinguish between the central (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous systems. Practical exercises include examining histological slides of nervous tissue and identifying structures under a microscope. Dissections of nerve specimens and hands-on activities help reinforce understanding. Proper staining techniques and labeling are emphasized to ensure accurate identification. This section is crucial for developing a strong foundation in neuroanatomy and its functional significance.
5.2 Understanding Reflexes and Nerve Impulses
Understanding reflexes and nerve impulses is crucial for grasping nervous system functionality. Reflexes are automatic responses to stimuli‚ involving sensory and motor neurons. Lab practicals focus on identifying reflex arcs and their components. Nerve impulses involve action potentials and synaptic transmissions. Students learn to differentiate between types of reflexes and analyze nerve impulse propagation using histological slides and simulations. This section emphasizes the integration of neural structures and their functional roles in maintaining homeostasis and responding to environmental changes.
5.3 Special Senses: Eye and Ear Dissection
Eye and ear dissection in Lab Practical 1 focuses on exploring the intricate structures of sensory organs. Students examine the eye’s layers‚ including the cornea‚ retina‚ and optic nerve‚ and the ear’s components‚ such as the tympanic membrane and cochlea. This hands-on activity aids in understanding how these organs detect light and sound. Histological slides and dissection tools help identify key features‚ correlating anatomical structures with their physiological functions in vision and hearing. This exercise enhances comprehension of sensory mechanisms and their roles in perception.
Respiratory and Circulatory System Practical
This practical focuses on identifying respiratory structures‚ examining the heart and blood vessels‚ and preparing blood smears for analysis‚ linking anatomy to circulatory and respiratory functions.
6.1 Identifying Respiratory System Structures
Identifying respiratory system structures involves examining the trachea‚ bronchi‚ and bronchioles‚ noting their branching patterns. Students learn to recognize alveoli‚ the diaphragm‚ and nasal cavity components. Understanding the larynx and its role in air passage is crucial. Proper identification techniques and histological slides are emphasized to differentiate structures. Interactive models and diagrams aid in visualizing airflow pathways. This section ensures a strong foundation in respiratory anatomy‚ essential for understanding gas exchange and breathing mechanisms. Regular practice with lab specimens and virtual tools enhances identification accuracy and comprehension of respiratory functions.
6.2 Circulatory System: Heart and Blood Vessel Identification
In the circulatory system section‚ students identify heart structures such as chambers‚ valves‚ and blood vessel types. Histological slides of arteries and veins are compared to observe differences in wall thickness and structure. Key features like the aorta’s elasticity and capillary thinness are highlighted. Practical exercises involve distinguishing between pulmonary and systemic circulation. Tools like diagrams and microscopes aid in understanding blood flow direction and vessel function. Hands-on identification of heart and vessel specimens is emphasized to reinforce circulatory system anatomy and physiology concepts effectively.
6.3 Blood Smear Preparation and Analysis
Blood smear preparation involves creating a thin film of blood on a slide‚ allowing it to dry‚ and staining it with Romanowsky dyes. This process helps differentiate blood cells. Under a microscope‚ students identify red blood cells (RBCs)‚ white blood cells (WBCs)‚ and platelets. WBC types‚ such as neutrophils‚ lymphocytes‚ monocytes‚ eosinophils‚ and basophils‚ are analyzed for morphology and abnormalities. Proper staining and smear techniques are emphasized to ensure accurate cell identification and diagnosis of conditions like anemia or infection.
Digestive and Urinary System Lab Exercises
Digestive and urinary system exercises involve organ identification‚ dissection‚ and functional analysis. Students explore structures like the stomach‚ intestines‚ liver‚ kidneys‚ and urinary bladder‚ linking anatomy to physiology;
7.1 Digestive System: Organ Identification and Functions
This section focuses on identifying key digestive organs such as the esophagus‚ stomach‚ small intestine‚ and liver. Students learn their roles in digestion‚ absorption‚ and nutrient processing. Practical exercises involve dissecting specimens to visualize structures and understand their functions. Emphasis is placed on recognizing histological features under a microscope and correlating anatomy with physiological processes. Understanding these concepts is crucial for mastering the digestive system in lab practical exams.
7.2 Urinary System: Kidney and Urinary Bladder Dissection
This section involves the dissection of the kidney and urinary bladder to explore their internal and external structures. Students identify key features such as the renal cortex‚ medulla‚ and pelvis in the kidney‚ and the layers of the bladder wall. The exercise emphasizes understanding the functional anatomy of these organs‚ including their roles in filtration‚ storage‚ and excretion. Practical skills include recognizing microscopic features and correlating them with physiological functions‚ such as blood filtration and urine storage.
7.3 Urinalysis and Its Significance
Urinalysis involves the examination of urine to assess kidney function and detect abnormalities. It includes physical (color‚ clarity)‚ chemical (pH‚ protein‚ glucose)‚ and microscopic (cells‚ crystals) analyses. This procedure helps identify conditions like diabetes‚ infections‚ or kidney damage. Students learn to perform tests‚ interpret results‚ and correlate findings with physiological or pathological states. Understanding urinalysis is crucial for diagnosing urinary system disorders and emphasizes the importance of lab skills in clinical practice.

Endocrine and Integumentary System Practical
This section explores the endocrine glands‚ their hormone functions‚ and the integumentary system‚ including skin layers and accessory organs like nails and hair. Practical exercises enhance understanding.
8.1 Identifying Endocrine Glands and Their Functions
This section focuses on recognizing key endocrine glands‚ such as the pituitary‚ thyroid‚ adrenal‚ pancreas‚ and gonads. Students learn to locate these glands‚ understand their hormone production‚ and link them to bodily functions like metabolism‚ growth‚ and reproduction. Practical exercises involve identifying gland structures in diagrams and specimens‚ correlating their roles in maintaining homeostasis. This hands-on approach reinforces the importance of the endocrine system in regulating various physiological processes.
8.2 Integumentary System: Skin Layers and Accessory Organs
This section explores the structure and function of the integumentary system‚ focusing on the layers of the skin (epidermis‚ dermis‚ hypodermis) and accessory organs like hair‚ nails‚ and glands. Students learn to identify these components in lab specimens and understand their roles in protection‚ thermoregulation‚ and sensation. Practical exercises involve examining skin samples under microscopes and correlating anatomical features with physiological functions‚ such as sweat and sebaceous gland secretion‚ to appreciate the system’s vital role in maintaining body integrity and overall health.
8.3 Hormone Regulation and Skin Histology
This section examines the relationship between hormones and skin health‚ focusing on how endocrine factors influence skin histology. Students learn to identify hormone-related changes in skin samples‚ such as variations in thickness‚ pigmentation‚ and glandular activity. Practical exercises involve analyzing histological slides to observe the effects of hormones like cortisol and estrogen on skin layers; Understanding these interactions is crucial for linking endocrinology with dermatology‚ preparing students to recognize hormonal impacts on skin integrity and function in clinical and laboratory settings.
Lab Practical Tools and Techniques
Essential tools include microscopes‚ dissecting kits‚ and slide preparation materials. Techniques involve proper specimen handling‚ accurate measurements‚ and efficient use of lab equipment for successful outcomes.
9.1 Using Dichotomous Keys for Identification
Dichotomous keys are essential tools for identifying biological structures. They provide a step-by-step process of elimination‚ guiding users through critical characteristics to accurately determine the specimen. By systematically comparing features‚ students can distinguish between similar structures‚ enhancing their observational skills. Regular practice with these keys improves efficiency and confidence during lab practicals. They are particularly useful for identifying bones‚ muscles‚ and histological samples‚ making them indispensable for anatomy and physiology lab success.
9;2 Proper Use of Lab Instruments and Equipment
Proper use of lab instruments and equipment is crucial for accurate observations and safety. Microscopes‚ dissecting tools‚ and histology equipment require precise handling. Always calibrate microscopes before use and handle slides gently to avoid damage. Dissecting tools should be used with care to ensure clean cuts and prevent accidents. Regular maintenance of equipment‚ like cleaning and storing properly‚ extends their lifespan. Familiarizing oneself with instrument functions and following safety protocols ensures efficient and effective lab work‚ enhancing the learning experience in anatomy and physiology.
9.3 Safety Protocols in the Lab Environment
Safety protocols are essential to prevent accidents and ensure a secure lab environment. Always wear personal protective equipment (PPE)‚ such as gloves and goggles‚ when handling specimens or chemicals. Properly label and store hazardous materials‚ and follow disposal guidelines. Familiarize yourself with emergency exits‚ fire extinguishers‚ and first aid kits. Avoid eating or drinking in the lab‚ and wash hands thoroughly after handling biological materials. Adhere to equipment safety guidelines‚ such as using tongs or heat-resistant pads for hot items. Regular safety drills and updates on protocols are crucial for maintaining a safe workspace.

Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Common mistakes in lab practicals include misidentification of structures‚ poor time management‚ and improper equipment use. Reviewing materials and practicing regularly can help avoid these errors.
10.1 Misidentification of Structures
Misidentification of structures is a common error in anatomy and physiology lab practicals. This often occurs due to inadequate preparation or insufficient familiarity with histological slides. Students may confuse similar-looking tissues or fail to recognize specific cellular features under the microscope. To avoid this‚ thorough review of lab manuals‚ regular practice with sample slides‚ and active participation in dissection exercises are recommended. Using dichotomous keys and seeking instructor feedback can also enhance accuracy in identifying structures. Consistent practice helps build confidence and reduces errors during exams.
10.2 Time Management During the Exam
Effective time management is crucial during anatomy and physiology lab practicals. Allocate equal time to each station‚ avoiding excessive focus on a single structure. Prioritize challenging sections and leave a few minutes for review. Skim through questions first to plan your approach. Practice timing during study sessions to build familiarity with exam pacing. Staying calm and organized ensures efficient use of the allotted time‚ reducing stress and improving performance. Proper planning helps cover all sections without rushing‚ leading to better accuracy and higher scores.
10.3 Improper Use of Lab Equipment
Improper use of lab equipment is a common mistake that can lead to inaccurate results or safety hazards. For instance‚ mishandling microscopes‚ such as improper focusing or slide preparation‚ can result in unclear observations. Similarly‚ using dissection tools incorrectly may damage specimens or cause injuries. Students must familiarize themselves with equipment functions and adhere to safety protocols. Neglecting to calibrate instruments or improperly storing supplies can also disrupt the lab workflow. Understanding proper techniques is essential to avoid errors and ensure a smooth‚ safe exam experience.

Tips for Success in Lab Practical 1
Active participation in lab sessions‚ regular practice‚ and seeking feedback from instructors are key to excelling in Anatomy and Physiology Lab Practical 1.
11.1 Active Participation in Lab Sessions
Active participation in lab sessions is crucial for mastering Anatomy and Physiology Lab Practical 1. Engage fully in dissections‚ microscope exercises‚ and group activities to enhance understanding. Asking questions and clarifying doubts during labs ensures a stronger grasp of concepts. Consistent engagement helps build confidence and improves practical skills‚ which are essential for success in the exam. Regular attendance and focused involvement in lab work lay a solid foundation for achieving high scores in the practical assessments.
11.2 Regular Practice and Review
Regular practice and review are essential for excelling in Anatomy and Physiology Lab Practical 1. Set aside time daily to review notes‚ identify structures‚ and practice lab techniques. Utilize flashcards‚ diagrams‚ and online resources to reinforce learning. Consistent review helps retain complex information and builds familiarity with lab equipment and procedures. By dedicating time to practice‚ students can confidently approach the exam‚ ensuring a thorough understanding of all covered topics and improving their ability to identify and analyze anatomical structures accurately.
11.3 Seeking Feedback from Instructors
Seeking feedback from instructors is crucial for improving performance in Anatomy and Physiology Lab Practical 1. Regularly discuss your progress with instructors to gain insights into areas needing improvement; They can provide personalized tips and clarify doubts‚ ensuring a stronger grasp of complex topics. Actively seeking feedback demonstrates initiative and helps tailor your study strategies to meet exam expectations. By addressing weaknesses early‚ you can refine your skills and approach the practical exam with confidence‚ ultimately enhancing your overall understanding and performance in the lab setting.
Resources for Lab Practical Preparation
Utilize textbooks like Guyton’s Physiology and Chaurasiya’s Anatomy for in-depth understanding. Explore online platforms offering virtual labs and practice exams to reinforce concepts and improve practical skills effectively.
12.1 Recommended Textbooks and Guides
Essential textbooks for anatomy and physiology include “Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology” and “B.D. Chaurasiya’s Human Anatomy.” These texts provide detailed explanations of human systems and structures. Additionally‚ lab manuals like “Anatomy and Physiology Lab Manual” by Teresa Stephan and “Practical Anatomy and Physiology” are invaluable for hands-on preparation. These resources offer comprehensive coverage of topics‚ ensuring a solid foundation for lab practical exams.
Atlases such as “Netter’s Atlas of Human Anatomy” are highly recommended for visual learning. These guides complement theoretical knowledge with high-quality images‚ aiding in the identification of structures during practical sessions. Utilizing these resources ensures thorough preparation for the lab practical‚ covering both theoretical and practical aspects effectively.
12.2 Online Resources and Virtual Labs
Online resources like McGraw Hill Education and Kenhub offer interactive anatomy diagrams and practice quizzes. Virtual labs‚ such as those provided by Labster and Anatomy.TV‚ enable students to explore 3D models and simulate dissections. These tools enhance understanding of complex structures and processes. Platforms like Visible Body and Physeo provide video tutorials and practice exams‚ aiding in self-assessment. Utilizing these resources ensures comprehensive preparation for lab practicals‚ offering flexible and engaging learning opportunities.
12.4 Practice Exams and Past Papers
Practice exams and past papers are invaluable for assessing readiness for Anatomy and Physiology Lab Practical 1. These resources simulate real exam conditions‚ helping students gauge their knowledge and identify weak areas. Websites like ATI TEAS Science Version 7 and Professor A&P Lab Channel offer practice exams specifically designed for lab practicals. Past papers from previous years provide insights into common question patterns and emphasize key topics. Regularly attempting these exams enhances problem-solving skills‚ time management‚ and familiarity with the exam format‚ ensuring better performance on the actual day.